How to Analyze X-ray Images: Techniques for Identifying Abnormalities and Anomalies
X-ray imaging is a crucial tool in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. It allows doctors to see inside the body and identify any abnormalities or anomalies that may be present. Analyzing X-ray images requires specialized knowledge and techniques to ensure accuracy and consistency in diagnosis.
Why Analyzing X-ray Images is Important
X-ray images provide a non-invasive method of examining internal structures and identifying any abnormalities. They are commonly used to diagnose conditions such as fractures, lung infections, and tumors. Early detection of these conditions can significantly improve treatment outcomes and increase the chances of recovery.
However, analyzing X-ray images is not always straightforward. The images can be complex and require a trained eye to interpret. Different techniques and tools are used to analyze X-ray images, including image enhancement, segmentation, and feature extraction.
The Importance of Proper Technique
It is essential to use the proper technique when analyzing X-ray images to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment. This requires knowledge of anatomy, pathology, and radiology, as well as specialized software and equipment.
In this article, we will explore some of the techniques used to analyze X-ray images and identify abnormalities and anomalies.

Preparing for Analysis
Before analyzing X-ray images, it is important to ensure that the images are of high quality and accurately depict the body part being examined. This involves understanding the anatomy of the body part being examined, as well as ensuring proper positioning and exposure settings.
Understanding the Anatomy of the Body Part Being Examined
One of the first steps in preparing for X-ray analysis is to have a good understanding of the anatomy of the body part being examined. This will help you to identify any abnormalities or anomalies that may be present in the images.
For example, if you are analyzing X-ray images of the chest, you should be familiar with the anatomy of the lungs, heart, and other structures in the chest area. This will allow you to identify any abnormalities or anomalies in these structures, such as fluid buildup in the lungs or an enlarged heart.
Ensuring Proper Positioning and Exposure Settings
In addition to understanding the anatomy of the body part being examined, it is important to ensure that the patient is properly positioned and that the exposure settings are appropriate for the type of image being taken.
Proper positioning is essential for obtaining accurate X-ray images. This involves positioning the patient in such a way that the body part being examined is in the correct position for the image to be taken. For example, if you are taking X-ray images of the knee, the patient should be positioned with their knee in a straight position and their foot pointing straight ahead.
Exposure settings are also important for obtaining high-quality X-ray images. Exposure settings determine how much radiation is used to create the image, and can affect the clarity and detail of the image. The exposure settings should be adjusted based on the type of image being taken and the size and density of the body part being examined.
| Body Part | Recommended Exposure Settings |
|---|---|
| Chest | Low kVp, high mAs |
| Abdomen | High kVp, low mAs |
| Extremities | Low kVp, low mAs |
By understanding the anatomy of the body part being examined and ensuring proper positioning and exposure settings, you can obtain high-quality X-ray images that are suitable for analysis and interpretation.
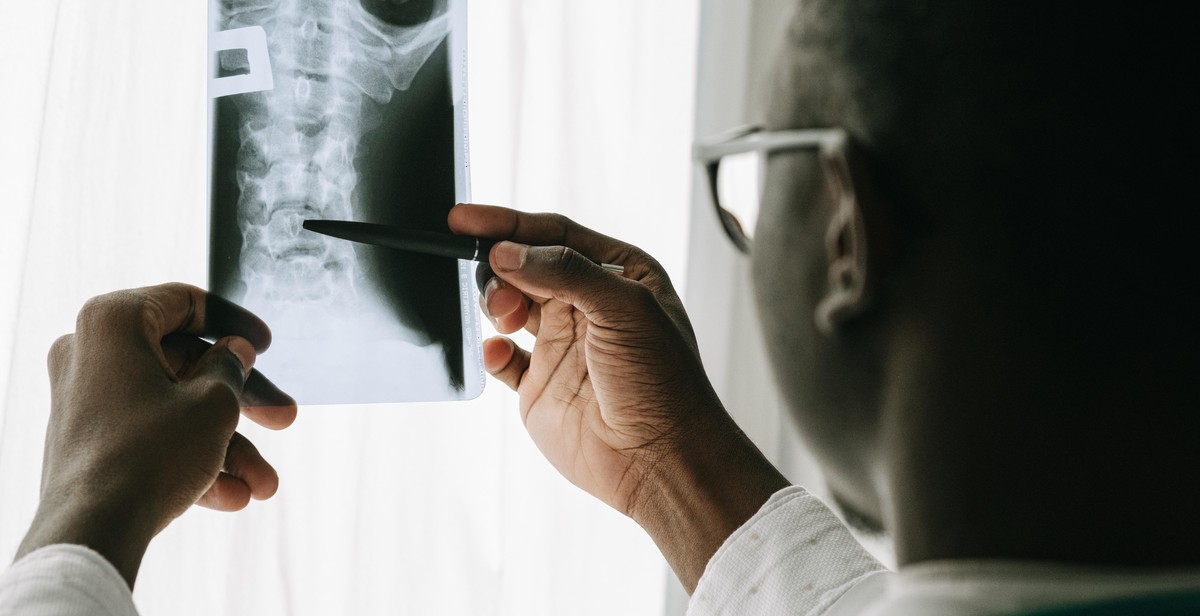
Analyzing X-ray Images
X-ray images are an essential tool used in the medical field to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions. An X-ray image is created by passing X-rays through the body, and the amount of radiation that passes through the body is detected by a special plate or film. The resulting image shows the internal structures of the body, such as bones and organs. Analyzing X-ray images requires a trained eye and specialized knowledge of anatomy and pathology.
Identifying Bone Fractures
One of the most common uses of X-ray images is to identify bone fractures. A fracture appears as a break in the bone on the X-ray image. The type of fracture can be determined by the shape and location of the break. For example, a spiral fracture may indicate a twisting injury, while a hairline fracture may be difficult to see but still be present.
Detecting Soft Tissue Injuries
X-ray images can also be used to detect soft tissue injuries, such as sprains and strains. While these injuries may not be visible on the X-ray image, they can be inferred by the presence of swelling or other abnormalities in the affected area. In some cases, a contrast dye may be used to highlight soft tissue injuries on the X-ray image.
Spotting Abnormalities in the Lungs
X-ray images are also used to spot abnormalities in the lungs, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and lung cancer. These abnormalities may appear as areas of increased or decreased density on the X-ray image. The shape and location of the abnormality can help determine the underlying condition.
Identifying Anomalies in the Digestive Tract
X-ray images can also be used to identify anomalies in the digestive tract, such as ulcers, tumors, and obstructions. A contrast dye may be used to highlight the digestive tract on the X-ray image. The shape and location of the anomaly can help determine the underlying condition.
| X-ray Image Analysis | Examples |
|---|---|
| Identifying Bone Fractures | Spiral, hairline, displaced, comminuted |
| Detecting Soft Tissue Injuries | Swelling, inflammation, tears |
| Spotting Abnormalities in the Lungs | Pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung cancer |
| Identifying Anomalies in the Digestive Tract | Ulcers, tumors, obstructions |
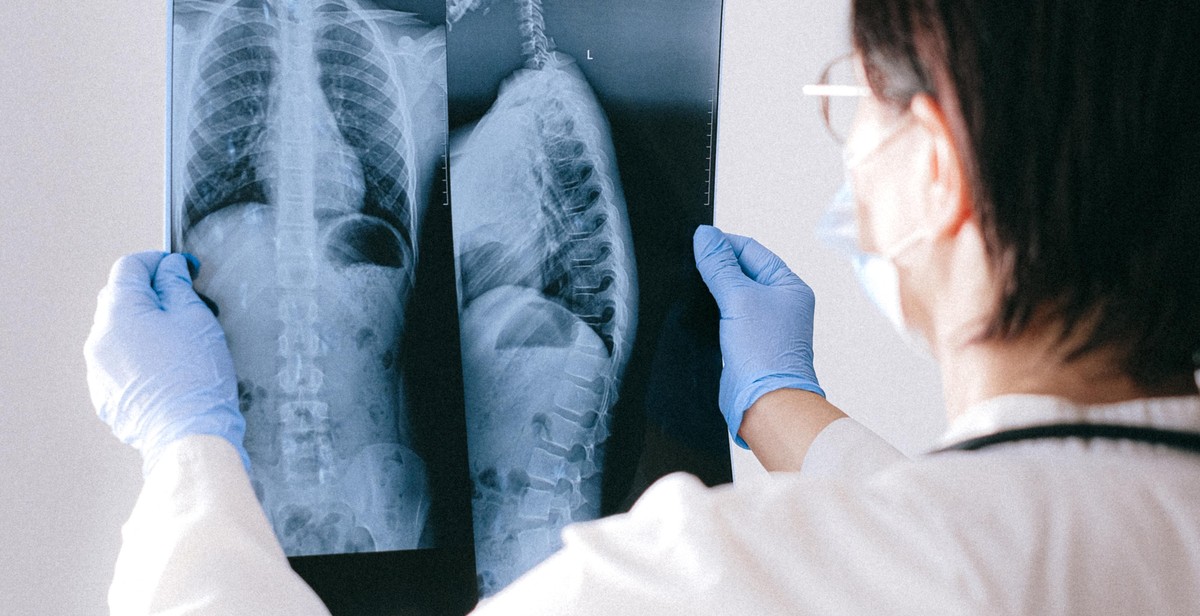
Additional Techniques for Analysis
While traditional X-ray imaging techniques are still widely used for diagnosing abnormalities and anomalies, there are additional techniques that can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the analysis process.
Using Contrast Agents for Enhanced Imaging
In some cases, using contrast agents can significantly improve the quality of X-ray images and make it easier to identify abnormalities and anomalies. Contrast agents are substances that are injected into the body to highlight specific areas or structures during imaging. They work by absorbing or reflecting X-rays differently than the surrounding tissue, which creates a contrast that enhances the visibility of the targeted area.
For example, iodine-based contrast agents can be used to enhance the visibility of blood vessels, organs, and other soft tissues. Barium sulfate can be used to highlight the digestive tract, while gadolinium-based contrast agents can be used to enhance the visibility of the brain, spine, and other nervous system tissues.
Before using contrast agents, it is important to consider any potential risks or side effects, such as allergic reactions or kidney damage. Patients should also inform their healthcare provider of any existing medical conditions or medications they are taking.
Employing Computer-Aided Detection (CAD)
Computer-aided detection (CAD) is a software-based tool that can analyze X-ray images and help identify abnormalities and anomalies that may be difficult to detect with the naked eye. CAD works by analyzing the patterns and characteristics of the X-ray image and comparing them to a database of known abnormalities and anomalies.
CAD can be particularly useful in cases where the radiologist or healthcare provider may be inexperienced or in cases where the abnormality or anomaly is subtle or difficult to detect. CAD can also help reduce the likelihood of false negative results, which can improve the accuracy of the diagnosis.
However, it is important to note that CAD is not a replacement for human interpretation and analysis. The results generated by CAD should always be reviewed and confirmed by a trained healthcare provider.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Contrast agents can enhance the visibility of specific areas or structures, making it easier to identify abnormalities and anomalies. | Contrast agents can pose risks and side effects, such as allergic reactions or kidney damage. |
| CAD can help identify abnormalities and anomalies that may be difficult to detect with the naked eye. | CAD is not a replacement for human interpretation and analysis. |
| CAD can reduce the likelihood of false negative results, which can improve the accuracy of the diagnosis. | CAD may generate false positive results, which can lead to unnecessary tests or procedures. |
Overall, using contrast agents and employing CAD can be effective techniques for enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of X-ray image analysis. However, it is important to consider the potential risks and limitations of these techniques and to always consult with a trained healthcare provider for proper interpretation and analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, analyzing X-ray images is a vital part of the diagnostic process for medical professionals. By using the techniques and tips discussed in this article, identifying abnormalities and anomalies in X-ray images becomes easier and more accurate.
It is important to remember to always follow proper safety protocols when handling X-ray equipment and images. Additionally, seeking the advice and expertise of a radiologist or other medical professional is recommended when interpreting X-ray images.
With the advancements in technology, there are now several software programs available that can assist in analyzing X-ray images. These programs can help identify abnormalities and anomalies that may be missed by the naked eye. However, it is important to remember that these programs should not replace the expertise of a trained medical professional.
Key Takeaways
- Proper technique is crucial when taking X-ray images.
- Understanding anatomy and physiology is important when interpreting X-ray images.
- Abnormalities and anomalies in X-ray images can indicate various medical conditions.
- Consulting with a radiologist or other medical professional is recommended when interpreting X-ray images.
- Software programs can assist in analyzing X-ray images, but should not replace the expertise of a trained medical professional.
| Techniques | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Proper positioning | Clear and accurate images |
| Comparison to previous images | Identify changes over time |
| Understanding anatomy and physiology | Accurate interpretation of images |
By utilizing these techniques and following proper safety protocols, medical professionals can improve their ability to accurately identify abnormalities and anomalies in X-ray images. This ultimately leads to better patient care and outcomes.
