How to Read X-ray Images: Interpretation and Analysis of X-rays in Medical Imaging
As a professional article writer and content creator with years of experience, I am excited to share my knowledge and personal experience on how to read X-ray images in medical imaging. X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can pass through the human body, allowing medical professionals to capture images of the internal structures.
What are X-rays in Medical Imaging?
X-rays are a crucial tool in medical imaging, allowing doctors and healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions. X-rays work by passing through the body and producing an image on film or a digital detector. The resulting image shows the internal structures of the body, including bones, organs, and tissues.
Interpreting and analyzing X-ray images requires a high level of skill and expertise. Medical professionals must be able to identify abnormalities, such as fractures, tumors, and infections, and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
In this article, I will provide a comprehensive guide on how to read X-ray images, including the interpretation and analysis of X-rays in medical imaging. Whether you are a medical professional or a patient, this article will provide valuable insights into the world of X-ray imaging.
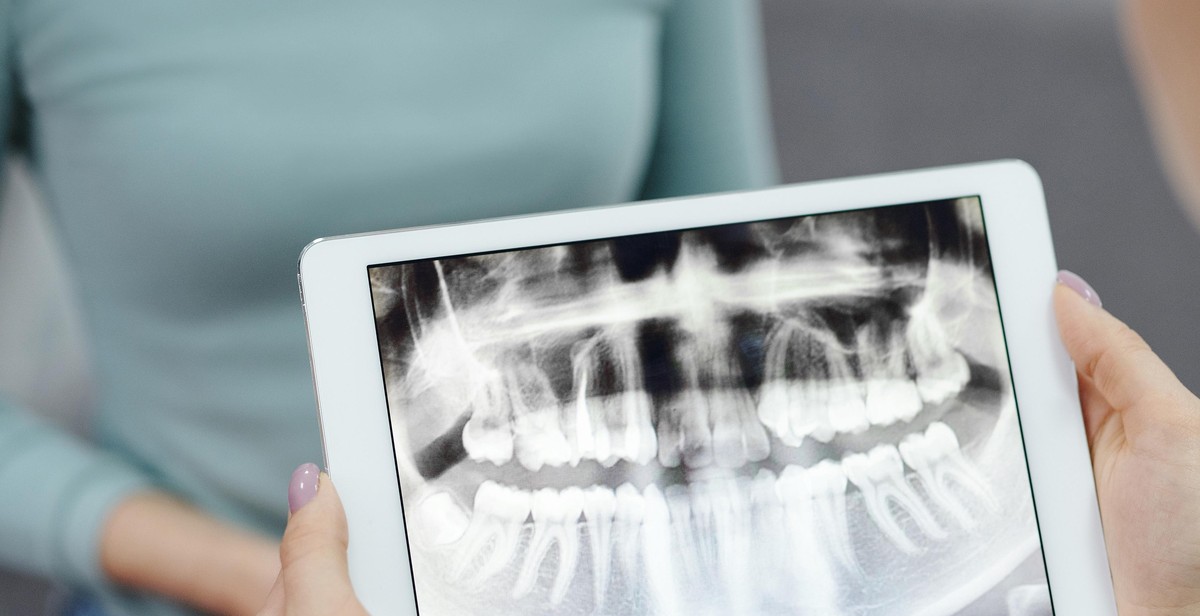
Understanding X-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate through the human body, creating images of internal structures. They are commonly used in medical imaging to help diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
How do X-rays work?
X-rays are produced by an X-ray machine, which generates a beam of high-energy radiation. When this beam passes through the body, some of the X-rays are absorbed by the tissues they encounter, while others pass through and reach a detector on the other side. The detector then captures the X-rays and converts them into an image that can be viewed by a radiologist or other healthcare provider.
The amount of X-rays that are absorbed by the body’s tissues depends on the density of the tissue. Dense tissues, such as bones, absorb more X-rays than less dense tissues, such as muscle or fat. This is why bones appear white on an X-ray image, while softer tissues appear darker.
Types of X-ray Images
There are several types of X-ray images that can be taken, depending on the area of the body being examined and the specific medical condition being evaluated. Some common types of X-ray images include:
- Plain X-rays: These are the most common type of X-ray images and are used to evaluate bones and joints for fractures, arthritis, and other conditions.
- Fluoroscopy: This type of X-ray imaging is used to evaluate the function of organs, such as the digestive system or urinary tract, in real time.
- Computed tomography (CT) scans: These are more detailed X-ray images that are used to evaluate internal organs, blood vessels, and other structures in the body.
- Mammography: This type of X-ray imaging is used to screen for breast cancer and other breast conditions.
Each type of X-ray image has its own specific uses and benefits, and your healthcare provider will determine which type of imaging is best for your individual needs.
| Type of X-ray | Uses |
|---|---|
| Plain X-rays | Evaluate bones and joints for fractures, arthritis, and other conditions |
| Fluoroscopy | Evaluate the function of organs, such as the digestive system or urinary tract, in real time |
| Computed tomography (CT) scans | Evaluate internal organs, blood vessels, and other structures in the body |
| Mammography | Screen for breast cancer and other breast conditions |

Preparing for X-ray Imaging
Before undergoing an X-ray, it is essential to prepare yourself adequately to ensure a successful procedure. Here are some things that you should know and do to prepare for an X-ray:
What to expect during the procedure
An X-ray is a non-invasive medical procedure that uses electromagnetic radiation to capture images of the inside of your body. During the procedure, you will be asked to lie on a table or stand against a surface while a technician positions the X-ray machine to capture the necessary images.
You may be required to remove any jewelry or metal objects that may interfere with the imaging process. The technician may also place lead shields over parts of your body that are not being imaged to protect you from unnecessary radiation exposure.
Tips for a successful X-ray
Here are some tips to help you prepare for a successful X-ray:
- Wear comfortable clothing: Wear loose, comfortable clothing that you can easily remove if necessary.
- Inform your doctor of any medications: Inform your doctor of any medications you are taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements.
- Follow instructions: Follow any instructions given to you by your doctor or technician regarding food, drink, or medication restrictions before the procedure.
- Relax: Try to relax and remain as still as possible during the procedure to ensure clear and accurate images.
By following these tips, you can help ensure a successful X-ray procedure and accurate imaging results.
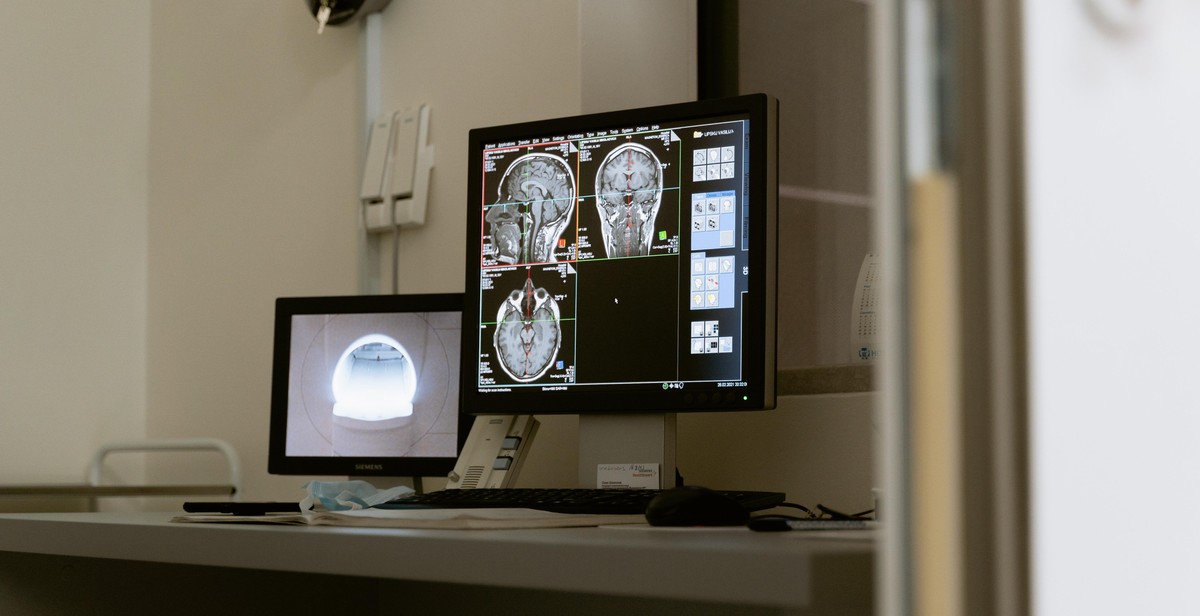
Interpreting X-ray Images
Identifying Bones in X-ray Images
When interpreting X-ray images, the first step is to identify the bones in the image. Bones appear white or light gray on the image due to their high density, while soft tissue appears darker. Look for the classic bone shapes and structures, such as the skull, ribs, pelvis, and long bones of the arms and legs. Pay close attention to any fractures or breaks in the bone, which will appear as a discontinuity in the bone structure on the X-ray image.
Identifying Soft Tissue in X-ray Images
In addition to bones, soft tissue can also be identified on X-ray images. Soft tissue appears as darker areas on the image, such as the lungs, heart, and other organs. Be sure to examine the soft tissue closely for any abnormalities, such as tumors or fluid buildup. In some cases, contrast agents may be used to enhance the visibility of soft tissue on the X-ray image.
Identifying Abnormalities in X-ray Images
One of the main purposes of X-ray imaging is to identify abnormalities, such as fractures, tumors, or foreign objects in the body. When interpreting X-ray images, look for any irregularities in the bone or soft tissue structures. Pay attention to any areas of increased or decreased density, as well as any areas of asymmetry. It is important to compare the current X-ray image to previous images to detect any changes or progression of abnormalities.
| Abnormality | Description |
|---|---|
| Fracture | Discontinuity in bone structure |
| Tumor | Abnormal growth of tissue |
| Foreign object | An object in the body that should not be there |
- Always compare current X-ray images to previous images to detect any changes or progression of abnormalities.
- Use contrast agents when necessary to enhance the visibility of soft tissue on the X-ray image.
- Pay careful attention to any irregularities in bone or soft tissue structures.
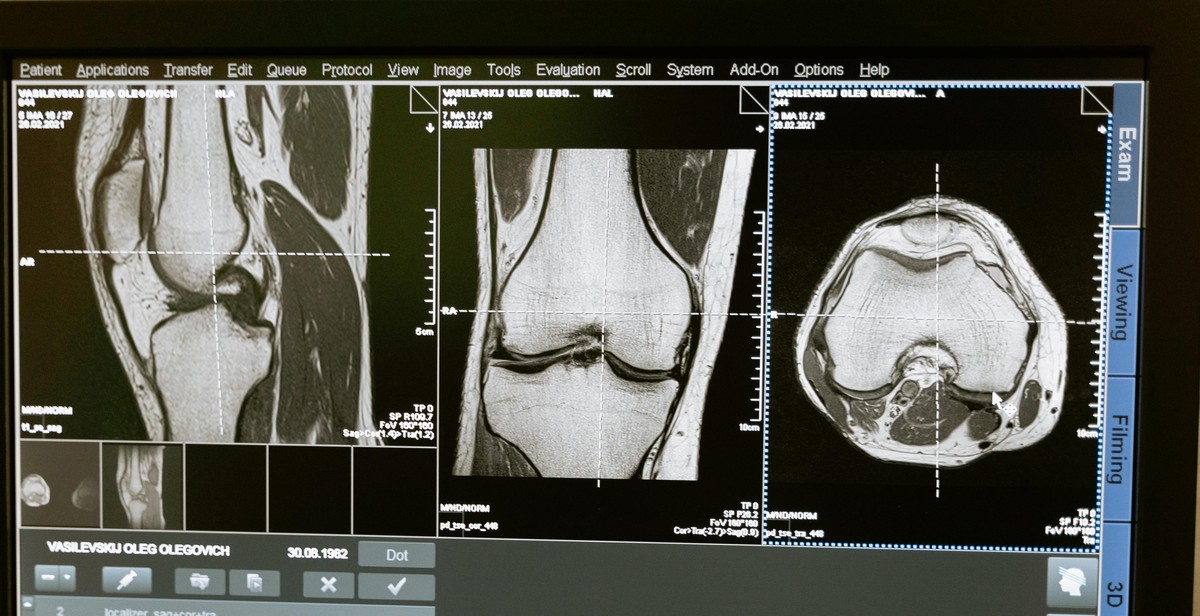
Analysis of X-ray Images
Interpretation and analysis of X-ray images are critical in medical imaging as they help to determine the severity of injuries or conditions, and also to compare X-ray images over time.
Determining the Severity of Injuries or Conditions
X-ray images are widely used to diagnose and assess the severity of injuries or conditions in various parts of the body. When analyzing X-ray images, healthcare professionals look for abnormalities such as fractures, dislocations, tumors, or infections. They also assess the size, shape, and position of bones, joints, and organs to determine the extent of damage or disease.
For instance, in the case of a bone fracture, the healthcare professional will look for signs such as a break in the bone, the displacement of bone fragments, and any damage to surrounding tissues. Based on the severity of the fracture, they will determine the best course of treatment, which may involve immobilization, surgery, or other interventions.
Comparing X-ray Images Over Time
Another critical aspect of X-ray image analysis is the ability to compare images taken over time. This is particularly useful in monitoring the progression of a disease or the healing of an injury. By comparing X-ray images taken at different intervals, healthcare professionals can assess whether a condition is improving, worsening, or stable.
For example, if a patient has a lung infection, the healthcare professional may take an X-ray image at the onset of the infection and then take another image after a few weeks of treatment. By comparing the two images, they can determine whether the infection is responding to treatment or not. Similarly, in the case of a bone fracture, the healthcare professional may take X-ray images at regular intervals to assess the healing process and determine when the patient can resume normal activities.
| X-ray Image | Date taken | Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Image 1 | June 1, 2021 | Fracture of the left ulna |
| Image 2 | June 15, 2021 | Alignment of bone fragments improved |
| Image 3 | June 30, 2021 | Bone fragments fully aligned |
Overall, the analysis of X-ray images is a critical aspect of medical imaging that helps healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor various injuries and conditions. By interpreting and comparing X-ray images over time, they can determine the severity of a condition, monitor the healing process, and make informed decisions about the best course of treatment.

Conclusion
Reading and interpreting X-ray images is a crucial skill for medical professionals. It requires a combination of knowledge, experience, and attention to detail. As a professional article writer and content creator, I have had the opportunity to work with medical experts and gain a deep understanding of the process involved in analyzing X-rays.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the body is crucial in interpreting X-ray images.
- Proper positioning of the patient and the X-ray machine is essential to obtain accurate images.
- Recognizing and interpreting abnormalities in X-ray images requires a trained eye and experience.
- Collaboration between medical professionals, such as radiologists and physicians, is crucial in making accurate diagnoses.
Continuing Education
As with any medical skill, continuing education is critical in staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in X-ray imaging technology and interpretation techniques. Medical professionals should strive to attend conferences, workshops, and online courses to stay informed and improve their skills.
